In the previous articles I have discussed 8 new features of ADO.NET 2.0, following are the remaining.
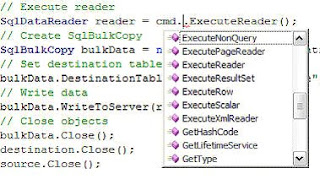
Now command object supports more execute methods. Besides old ExecuteNonQuery, ExecuteReader, ExecuteScaler, and ExecuteXmlReader, the new execute methods are ExecutePageReader, ExecuteResultSet, and ExecuteRow.
Figure 2 shows all of the execute methods supported by the command object in ADO.NET 2.0.
Figure 2. Command's Execute methods.
10. Improved Performance for DataSet Remoting
If we think about ADO.NET 1.x DataSet, the major problem which is DataSet Serialization. Microsoft has worked lots on this part and they have improved the performance of Serialization a lot. In ADO.NET 1.x, Serialization of DataSet will happen in XML format. Even in ADO.NET 2.0, by default it happens in XML format. But there is an option to change the Serialization format to Binary using property called "SerializationFormat". Look at the following code.
10. Improved Performance for DataSet Remoting
If we think about ADO.NET 1.x DataSet, the major problem which is DataSet Serialization. Microsoft has worked lots on this part and they have improved the performance of Serialization a lot. In ADO.NET 1.x, Serialization of DataSet will happen in XML format. Even in ADO.NET 2.0, by default it happens in XML format. But there is an option to change the Serialization format to Binary using property called "SerializationFormat". Look at the following code.
Dim format As New Binary.BinaryFormatter
Dim ds As New DataSet ds = DataGridView1.DataSource
Using fs As New FileStream("c:\sar1.bin", FileMode.CreateNew)
ds.RemotingFormat = SerializationFormat.Binary
'Other option is SerilaizationFormat.XML
'Other option is SerilaizationFormat.XML
format.Serialize(fs, ds)
End Using
In the above code snippet, we are serializing the dataset into filestream. If we look at the file size difference between XML and Binary formating, XML formating is more than three times bigger than Binary formating. If we see the perfomance of Remoting of DataSet when greater than 1000 rows, the binary formating is 80 times faster than XML formating.
11. DataSet and DataReader Transfer
In ADO.NET 2.0, we can load DataReader directly into DataSet or DataTable. Similarly we can get DataReader back from DataSet or DataTable. DataTable is now having most of the methods of DataSet. For example, WriteXML or ReadXML methods are now available in DataTable also. A new method "Load" is available in DataSet and DataTable, using which we can load DataReader into DataSet/DataTable. In other way, DataSet and DataTable is having method named "getDataReader" which will return DataReader back from DataTable/DataSet. Even we can transfer between DataTable and DataView. Check out the following example,
Dim dr As SqlDataReader
Dim conn As New SqlConnection(Conn_str)
conn.Open()
Dim sqlc As New SqlCommand("Select * from Orders", conn)
dr = sqlc.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection)
Dim dt As New DataTable("Orders")
dt.Load(dr)
12. Batch Updates
In previous versions of ADO.NET, if we do changes to DataSet and update using DataAdapter.update method. It makes round trips to datasource for each modified rows in DataSet. This fine with few records, but if there is more than 100 records in modified. Then it will make 100 calls from DataAccess layer to DataBase which is not acceptable. In this release, MicroSoft have changed this behaiour by exposing one property called "UpdateBatchSize". Using this we can metion how we want to groups the rows in dataset for single hit to database. For example if we want to group 50 records per hit, then we need to mention "UpdateBatchSize" as 50.
12. Batch Updates
In previous versions of ADO.NET, if we do changes to DataSet and update using DataAdapter.update method. It makes round trips to datasource for each modified rows in DataSet. This fine with few records, but if there is more than 100 records in modified. Then it will make 100 calls from DataAccess layer to DataBase which is not acceptable. In this release, MicroSoft have changed this behaiour by exposing one property called "UpdateBatchSize". Using this we can metion how we want to groups the rows in dataset for single hit to database. For example if we want to group 50 records per hit, then we need to mention "UpdateBatchSize" as 50.
13. Common Provider Model
In our application if want to implement provider independent DataAccess, then we need to write our own factory classes for returning the required objects like connection, command. And for implementing this feature only provider independent interface were available in the previous releases. But in ADO.NET 2.0, we have separate factory classes for managing common provider model. A new class "DbProviderFactory" is included in this release which has two methods. One method "GetFactoryClasses" to get all the provider installed in that machine and other one "GetFactory" will be used to get provider specific object by providing provider name as paramter.
Check out the following example, in which without knowing which provider we are going to work on we are fetching values from database. We need to pass only "Providername" which can configurable and which can change.
Dim pf As DbProviderFactory pf = DbProviderFactories.GetFactory(providername)
Using dbc As DbConnection = pf.CreateConnection
dbc.ConnectionString = Conn_str dbc.Open()
Dim comm As DbCommand = dbc.CreateCommand
comm.CommandText = "Select * from orders"
Dim dr As DbDataReader = comm.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection)
Dim ldt As New DataTable("Orders") l
dt.Load(dr)
End Using
14. Bulk Copy
If we think of bulk copy i.e. if we want to move some data from one datasource to another datasource. If will simply think of doing this in database, since we dont have much options in the previous release. But in ADO.NET 2.0, we can do this from DataAccess Layer itself.
New class called "SQLBulkCopy" is included in this release which will do this work for us. Using this class we can metion which datasource we want to copy and to which destination table we want to copy. We can even map the columns between tables, by default it will copy columns to columns. Check out the following example,
Dim dr As SqlDataReader
Dim conn As New SqlConnection(Conn_str)
Dim conn1 As New SqlConnection(Conn_str1)
conn.Open()
conn1.Open()
Dim sqlc As New SqlCommand("Select * from Orders", conn)
'dr = sqlc.ExecutePageReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection, 10, 10)
dr = sqlc.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection)
dr = sqlc.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection)
Dim dt As New DataTable("Orders")
Dim bulkcopy As New SqlBulkCopy(conn1)
bulkcopy.DestinationTableName = "MVPOrders"
bulkcopy.WriteToServer(dr)
15. Multiple Active ResultSets
Using this feature we can have more than one simultaneous pending request per connection i.e. multiple active datareader is possible. Previously when a DataReader is open and if we use that connection in another datareader, we used to get the following error "Systerm.InvalidOperationException: There is already an open DataReader associated with this connection which must be closed first". This error wont come now, as this is possible now because of MAR's. This feature is supported only in Yukon.
16. Conclusion
ADO.NET 2.0 provides many new and improved features for developers to improve the performance and reduce the code. In this article, I discussed top 15 features of ADO.NET 2.0
No comments:
Post a Comment